Sometimes you have a book that is just so loved. We have a few VERY loved books in our house and one of those books with the dog-eared corners is Dr. Seuss’ Wacky Wednesday. We used the book in a visual perceptual activity and worked on the skills needed for handwriting. Visual perception is made up of many different skill areas that are used in virtually every functional task we perform. Handwriting is just one of those tasks that relies on appropriate development of visual perception. Kids can use creative activities like hidden pictures and books like Wacky Wednesday to improve visual perception. Try this Wacky Wednesday Visual Perception Activity and have fun working on handwriting skills in a wacky way!

Wacky Wednesday Visual Perception Activity
Visual Perceptual Skills Developed by Completing Hidden Pictures
Visual Perception Skills
Build these Visual Perception Skills by working on hidden picture puzzles
Wacky Wednesday Visual Perception
The book is one that we were handed down in a bin of clothes and toys that another child had outgrown. It was apparent that the copy of Wacky Wednesday was a favorite book for this other child. When we started reading it, we were hooked too!
Use the book to visually scan and locate funny items while addressing the visual perceptual skills needed for handwriting. Then, ask kids to use those funny items they’ve found to work on handwriting skills. Kids can list out the funny items that are wacky. So, while searching and finding the funny images on each page, they can build the visual perceptual skills needed for handwriting. Then, they can visually shift to write lists while addressing neatness and legibility in written work.
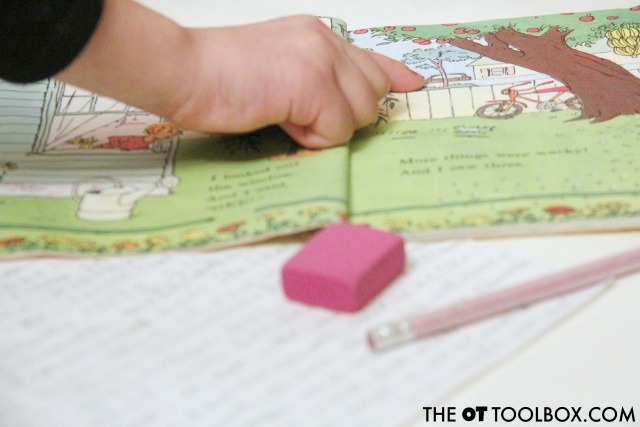

Many times, a motivating subject or activity can be just the thing that helps kids want to practice handwriting. Use the funny book that is Wacky Wednesday as a motivator.
If you are looking for more creative ways to work on the visual perception skills addressed in hidden pictures and relay them into handwriting skills, you are in luck!

Hidden Pictures Handwriting Workbook
I’ve created this Hidden Pictures Handwriting Workbook to address visual perceptual skills through hidden pictures. In this workbook, you’ll find two separate puzzles and related handwriting activities that can help kids address the visual perceptual skills noted above. By completing this 11 page workbook, kids can use creative handwriting activities and themed writing prompts to practice written work in a fun way.
What’s in the Hidden Pictures Handwriting Workbook?
- 11 pages of activities
- 2 hidden pictures puzzles
- 8-9 themed writing prompts for each puzzle
- Activities to promote visual shift, visual memory, visual discrimination, visual-figure ground, and form constancy
- Digital file that you can print or use on your tablet
We used the Hidden Pictures Handwriting Workbook on our touch laptop screen. Using the workbook on a tablet or touch device allows kids to visually scan and address those visual perception skills without printing out the color images.
This would be a great activity for a group in the classroom or for kids who need an at-home activity.
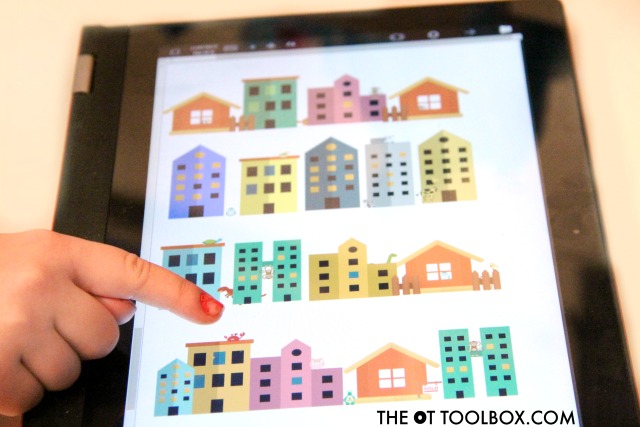

This is a digital file.
Get your copy of Hidden Pictures Handwriting Workbook for $4.99.
Looking for more ways to celebrate Dr. Seuss? Try the books in the Virtual Book Club for Kids series:
Alphabet Puzzles from Sea of Knowledge
Would You Eat This? A Green Eggs & Ham Activity from Sunny Day Family
Horton Hears a Who Listening Activities from JDaniel4’s Mom
Color Mixing Truffula Trees Art Project from School Time Snippets
Exploring Shapes and Silhouettes – The Shape of Me and Other Stuff from To Be a Kid Again
Ten Apples Up on Top Printable Math Activity from The Moments at Home
Cat in the Hat Inspired Popsicles from View from a Step Stool