Recently, I had the opportunity to try a set of adaptive grip crayons and I had to share this therapy tool. Below, you’ll find information on the adapted grip crayons created by Effortless Art and strategies to impact carry over of handwriting goals, or just specifically pencil grasp and crayon grasp when writing or coloring.
We also used these fun crayons for the 3 Crayon Challenge. Read below to see how to use a 3 crayon challenge to work on carryover of pencil grasp and a grasp activity that kids will love to do! You’ll want to check out our recommendations for the best crayons based on age, development, and fine motor skills, too.
You can use these coloring strategies on coloring activities like our President’s Day coloring pages (great for any US holiday!).
Teach Carryover of Pencil Grasp and Grasp When Coloring

When it comes to teaching kids to maintain a functional pencil grasp on a pencil or grasp on a crayon, one of the absolutely BIGGEST challenges for therapists is figuring out how to get kids to carryover the skills they accomplish in therapy sessions. A child may write or color with a functional pencil grasp when they are working one on one with an occupational therapist, but as soon as they are on their own for a writing or coloring task, the pencil grasp or grasp on the crayon is out the window! They revert back to the comfortable or easiest grasp they are used to.
This lack of carryover with pencil grasp is especially apparent when kids are creating novel work. You may notice this lack of carryover when a student is required to free-write a journal page or complete a short essay paragraph without copying from a source. The functional and efficient pencil grasp is the first to go!
The same situation occurs when a child is coloring. When a child colors, they may complain of fatigue after a few minutes. This is especially true for the child with hand weakness or fine motor deficits. They usually revert to their atypical grasp patterns that impact function and distal mobility when coloring.
Over in our Sweet Ideas for Handwriting Help group, the carryover and consistency issue comes up again and again. So often, therapists have told me their biggest challenge with working on a functional grasp is the lack of carryover.

What is a functional grasp?
So, when it comes to helping kids maintain a functional grasp on a pencil or crayon, there are a few tricks of the trade that can help. Today, we’re going to talk about how to help kids maintain a functional grasp when coloring.
Below are tips and tricks that help kids carryover a grasp that promotes a safe and efficient grasp when coloring.
Related Read: Read more about the many benefits of coloring here.
First, let’s talk about what makes up a functional grasp when coloring.
For the child who reverts to an atypical grasp when coloring, there can be a few things going on (click on each link below to read more about these specific underlying areas related to crayon grasp):
- Weak hands
- Closed thumb web space
- Hyper-extended joints
- Poor distal mobility (The child uses their shoulder, forearm, or wrist to color rather than the fingers to move the crayon)
- Poor separation of the sides of the hand

How to teach carryover of a functional grasp when coloring
Use these tips to teach kids to carryover the grasp skills they’ve learned in therapy or in on-on-one sessions when coloring:
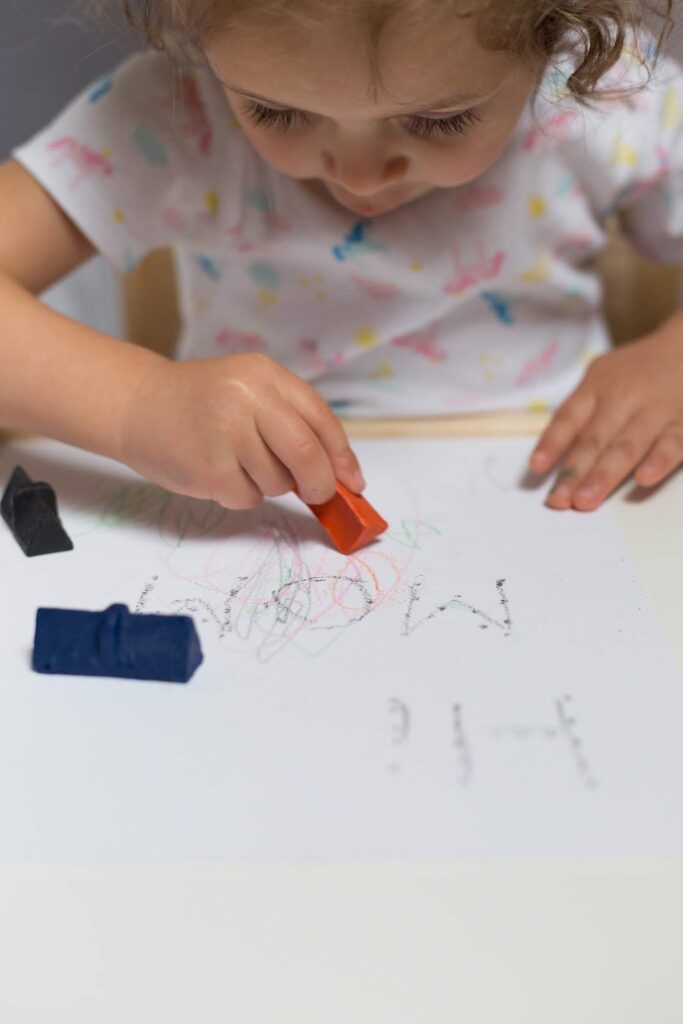
We used Effortless Art crayons, which are molded and adaptive grasp crayons to work on these skills. Amazon affiliate links are included below.
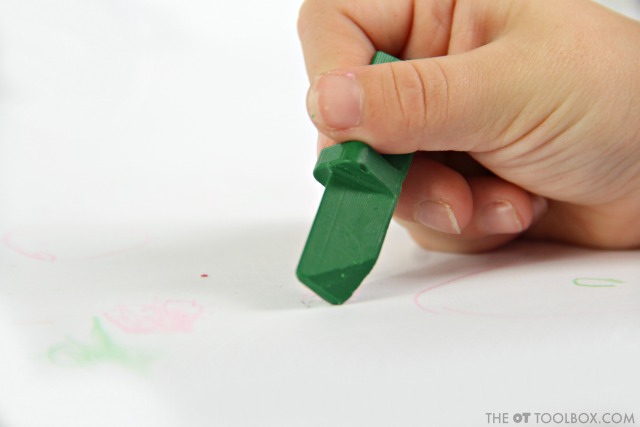

1. Use built-in adapted grip on molded crayons to use between color changes. The built-in molding of Effortless Art crayons are perfect for helping kids easily switch between different colors while using the natural built-up grip on the shaft of the crayon. In fact, the Effortless Art crayons have a patent pending design which ensures that no matter how your child picks up a crayon, they’ll have proper grip and finger placement so they can effortlessly begin coloring right away.

2. Promote distal mobility with a smaller coloring space to promote more precision and distal movement. The Level 2 Effortless Art crayons have a beveled edge that enables more refined precision for the advanced colorer! Asking kids to color in a smaller space encourages movement of the thumb and fingers to move the crayon as opposed to large movements that use the forearm or upper arm.

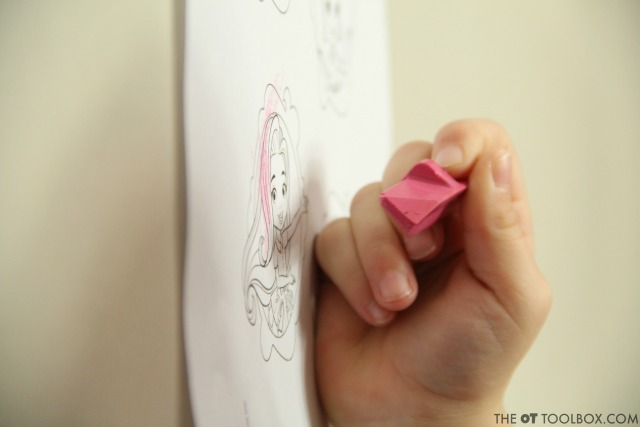
3. Use smaller crayons that fit in the thumb web space and promote opposition of the thumb to the pointer finger. One of the best tips to promote a functional grasp and separation of the sides of the hand is to use a smaller writing utensil. The shape and size of the Effortless Art crayons are small enough to fit in the hand while promoting opposition of the thumb to the pointer finger. Unlike larger molded crayons (like rock crayons or egg-shaped crayons) that are small but don’t allow for true opposition, the Effortless Art crayons have a molded shape that positions the precision side of the hand on the crayon every time. Now that is carryover and consistency!

4. Elevate coloring pages on an easel or wall. An elevated position on a vertical surface puts the wrist into an extended position and pulls the thumb and pointer finger into a functional position. A DIY slant board works well too! In fact, ensuring consistency and carryover is easy if you use the DIY version to enhance wrist extension when coloring. If you hang a coloring page on a wall, tape a big sheet of paper under the coloring page first to prevent wall markings.
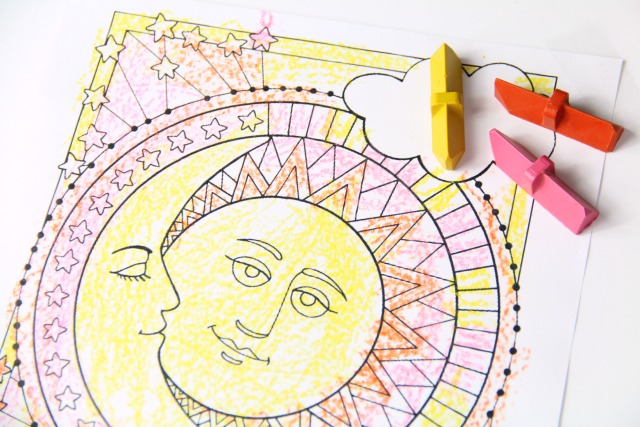

5. Make it fun! Like anyone, kids are intrinsically motivated by interests. I know my own kids are very into the three marker challenge that is taking over YouTube. So, why not make it a 3 crayon challenge and get the kids in on the challenge action? They will be motivated to do their best coloring, while switching colors and getting lots of crayon grasp practice in!
3 Crayon Challenge

Play the 3 Crayon Challenge to sneak in the skills kids need to maintain consistency and carryover with grasp on the crayon. Here’s how to play (It’s pretty easy!):
1. Close your eyes.
2. Pick 3 crayons.
3. Color a whole page with the three crayons.
Check out this video we created:
The 3 Crayon Challenge to teach carryover of pencil grasp

So, how does this fun challenge help kids carryover and use a functional grasp on crayons or pencils when writing? Well, coloring has so many benefits when it comes to strengthening the hands. Switching between the 3 crayon colors offers many opportunities to practice a functional grasp on the crayons. Additionally, kids can work on the visual motor skills needed for precision and line awareness when coloring.
We took the 3 crayon challenge up a notch and taped our picture to the wall. Coloring on a page on the wall really provides a therapeutic benefit to the task of coloring! Coloring on a vertical surface puts the arm, wrist, and hand into a position that promotes a functional pencil grasp. It encourages a tripod grasp, strengthens the arches of the hands, and separates the sides of the hand. What a powerhouse activity!
Using the Effortless Art molded crayons made this 3 Crayon Challenge an even better occupational therapy activity because there were so many opportunities to practice a functional grasp in a fun way!

More information about the Effortless Art crayon lines and the specific crayons:
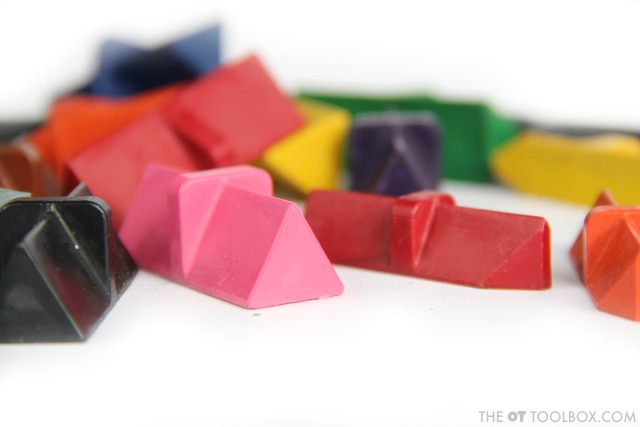

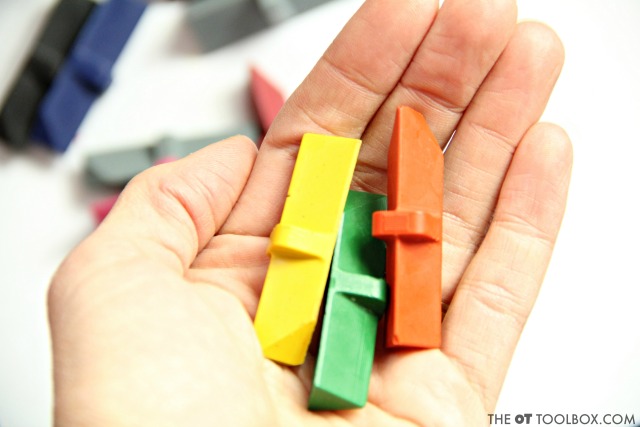
We had a blast trying out the Effortless Art crayon lines. The Level 1 version is great for beginners who are just beginning to progress through grasp development. The natural finger placement on the ridge or just below the ridge on the crayon allows for an open thumb web space, natural opposition of the thumb to the pointer finger, and placement of the middle finger as a support. This positioning pulls the precision side of the hand onto the crayon while allowing the power side of the hand to support the hand while coloring.
When this positioning is used on the crayon, the arches of the hand are developed, allowing for improved endurance when coloring.
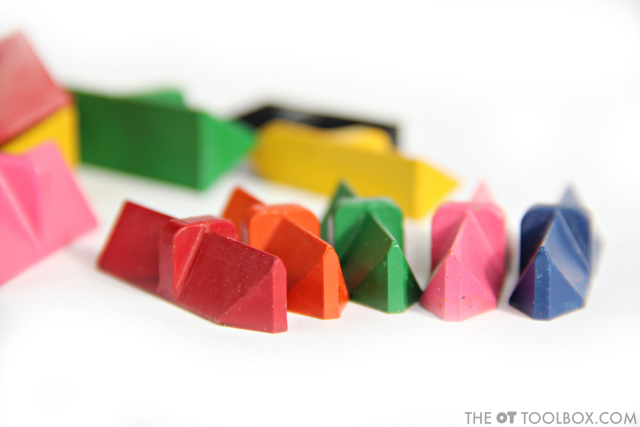

The second level of crayons is the Level 2 version, which has a smaller crayon shaft and shorter length. It’s also got a beveled edge which allows for coloring in smaller spaces and with more precision and distal mobility. These crayons can be purchased on the Effortless Art website, and should be available on Amazon soon.
Here are a few more features of the Effortless Art crayons and specific product features:
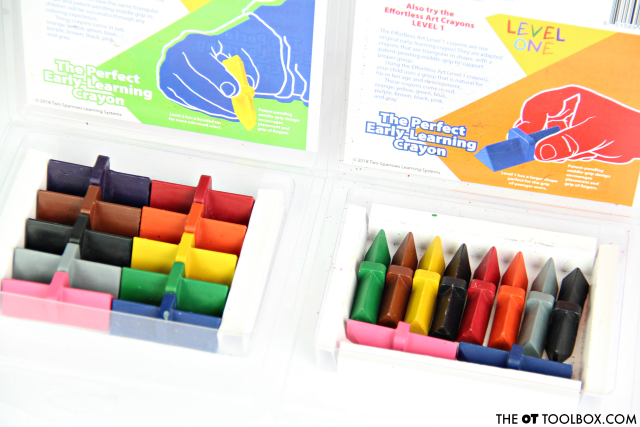

How does increased attention span when coloring sound? Recent studies have shown that children’s attention spans increase 20% to 60% when using Effortless Art Crayons compared to normal crayons.
Effortless Art Crayons are proud to donate to non-profit arts and early learning organizations and institutions are made from 100% recycled crayons.
You can find additional information on the crayons on the Effortless Art website. You’ll find that the crayons are available in packs of 5, 10, 60, 100, 120, and 200 on the website.
Have any questions? Direct customer questions about the Effortless Art crayons, interest in additional information on our products, or requests for additional information regarding the use of the crayons, to Effortless Art. The customer service team would be happy to review any questions. Large orders made by schools or other interests may purchase from the website where volume pricing is available.
Need a large order? This bucket of 60 crayons would be perfect for the classroom!