A term you may have heard when it comes to sensory processing is sensory dysregulation. What does this mean? Are there clues for dysregulation? We all have differing sensory needs, and dysregulation can look like different things for everyone. Have you ever wondered about specific sensory strategies for regulation to support a dysregulated sensory system? We’ll cover all of this in this post.

Sensory Dysregulation
Remember your last temper tantrum? Do you remember what it felt like to be suddenly so sad, mad, and completely out of control? Most of us probably had our last true temper tantrum more recently than we care to admit.
A majority of those emotional outbursts were probably exacerbated due to a number of reasons; lack of sleep, poor diet, undesirable environment, discomfort, or pain. Deciphering the difference between a tantrum and sensory meltdown is a must.
One ongoing debate in the pediatric therapy world is discussing what behaviors are due to sensory-related reactions, and what behaviors are due to something else. How many toddlers (or teenagers!) temper tantrums may actually be related to their sensory experience? If it really is sensory-based, then what are the solutions?
The OT Toolbox is here to do our best to answer your sensory-related questions. A great first step in determining whether unwanted behaviors are based on sensory experiences, is to learn about what sensory dysregulation is. To get started, here is an article about sensory processing red flags.
Playing a huge role is understanding self regulation and the ability to select and implement self regulation strategies based on sensory needs.
WHAT IS SENSORY DYSREGULATION?
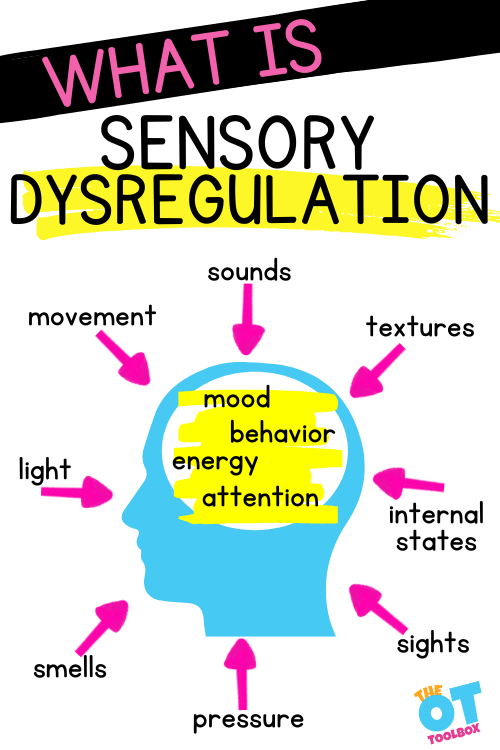
Sensory dysregulation refers to a mind or body state which occurs when the body is out of balance due to experiences in the sensory environment. Think about how sounds, textures, exercise, movement, smells, light, and other input can affect your mood. Sensory dysregulation is the result of either too much or too little stimulation for best functioning or self-regulation.
Read more about mood and affect and how these terms are connected to sensory dysregulation.
It’s more than sensory touch and the input we receive through our skin. It’s the inability to regulate sensory input from ALL the sensory systems.
A key component outcome of sensory dysregulation is self-regulation. There are many ways to define self-regulation, but generally, it is one’s ability to remain at an acceptable level of emotion, energy, behavior, and attention – given the demands of their environment.
In order to achieve self-regulation, one must also have good sensory regulation.
Sensory dysregulation is something that anyone can experience, and most people probably have experienced a level of sensory dysregulation to some degree.
Everyone has sensory preferences, like how loud they listen to music, or if they enjoy lots of hugs. If your preference is to have less, your systems would become out of balance with the music too loud or people getting too touchy.
Each of us has our own limits given any situation – but once you are in tune with your body’s needs, you know when it has become too much. When the system is unbalanced, maladaptive behaviors (tantrums) occur, if no coping strategies are implemented. We covered this individualized preferences and nuances of neurodiversity in greater detail in our post on Sensory Diets for Adults.
People with sensory processing disorder, which is an issue on a larger scale that affects a much smaller portion of the population, feel dysregulated more often and have far less ability to self-regulate. While sensory processing disorders can exist in isolation, they may be most prevalent in those with Autism or ADHD.
Check out our resources at the end of this article for great coping tools!
WHAT DOES DYSREGULATION LOOK LIKE?
Sensory dysregulation, much like emotional dysregulation, feels uncontrollable. Something is “wrong” and a person may not know what is causing them to feel “off”, or how to solve the problem. Sensory dysregulation may look and feel similar to emotional or behavioral dysregulation, that can cause temper tantrums.
The main difference is that sensory experiences are the root cause of the behavioral responses – not social disagreements or the like. It is complicated to tease out whether the issue is behavior or sensory. Look first at the triggers.
A simpler way to understand of sensory dysregulation, is by breaking it down into two categories: over-responsiveness or under-responsiveness to the environmental stimuli.
- Over-responsiveness may look like: sensory avoidant behaviors such as excessive covering of the ears, hiding, avoiding touch, or extreme picky eating. The body may be responding too much to the incoming information. One reaction is to avoided it to, remain at baseline.
- Under-responsiveness may look like: sensory seeking behaviors such as excessive or repetitive body movements, touching everything, making sounds, or licking/chewing on non-food items. Pushing other students while waiting in line. The body may be responding too little to typical input, to the point that the seeker looks for more of it to remain at baseline.
It is important to begin to recognize sensory over-and-under responsiveness and the role it plays in sensory regulation. Understanding what kind of behaviors a child has, will allow you to choose the right remedy.
- Over-responsive → Sensory Avoider → Need for less
- Solution – calming activities, breathing exercises, variety of activities to slowly increase comfort level
- Under-responsive → Sensory Seeker → Need for more
- Solution: heavy work, brain breaks, fidget tools, variety of sensory experiences
Resources from the OT Toolbox for Deep Breathing, Self-Regulation activities, Emotional Learning and Regulation, and the Sensory Lifestyle Handbook are a perfect starting point.
SENSORY DYSREGULATION IS NOT:
Sensory dysregulation is NOT the same as behavioral or emotional dysregulation, which may look like:
Not sensory dysregulation:
- Crying at the store after they were told “no”
- Pushing their brother after he took their toy
- Eating all foods but never what the family is eating
- Dumping/throwing toys after being told it’s time to clean up
- Covering their ears during a fire alarm
- Screaming after a sibling teased them
You may be thinking, wait a minute…some of those actions are sensory-based behaviors!
You are correct! However, just because something is related to the sensory experience, does not always mean that sensory dysregulation is occurring.
As an example; the sound of a fire alarm is loud auditory input, however, covering your ears during a loud sound is a normal response. If there is more of a reaction than that, for instance, if a child is inconsolable or unable to move on after the fire alarm, that may be considered sensory dysregulation.
Sensory Dysregulation Symptoms
When symptoms of sensory dysregulation is in question, you should be asking:
- What does the environment look like? Feel like?
- What is the child communicating with their actions?
- When and where does this behavior typically occur? In what similar situations does it not occur?
Some behaviors, like pushing, can be tricky to determine if it is sensory or behavior; Look at the trigger. The proprioceptive system can be dysregulated. Is the child pushing for sensory reasons?
- Bumping into things during play, crashing often, seemingly unaware of their body? Then they may have some sensory dysregulation going on that is increasing their need for input. Pushing people who get too close, hugging too hard, or bumping into people, may also be signs of sensory dysregulation.
- If a child pushes a friend after they did something mean, that is just poor social skills.
HOW CAN YOU support Sensory Dysregulation?
If a child’s sensory system is dysregulated, there is good news: there are many ways to help! There is a catch though – there is no “one size fits all”. Trial and error is the name of the game with sensory interventions.
Once you and your child find out what works for them and their changing environments, they will have a deeper understanding of themselves, and display improved behaviors in no time!
Check out these resources for sensory integration, calming exercises, self-regulation activities, and more! Also be sure to read our blog post on Ayres Sensory Integration for information on the theory behind this process, and how it all works together. It’s fascinating!
Tactile Sensory Input:
Heavy Work/ Propceptive Sensory Input:
- Sports Therapy
- Construction Truck Brain Breaks
- Superhero Gross Motor Activity
- Virtual Heavy Work
- Dinosaur Movement Cards
Vestibular Sensory Input:
Combined Sensory Input:
Deep Breathing Activities:
- Breathing & Relaxation
- Deep Breathing Print & Go
- Rainbow Deep Breathing Tool
- Spiderweb Breathing Freebie
- Snow Globe Breath Awareness
Mindfulness:
If you have tried everything, and are feeling a bit lost, you are not alone! Sensory dysregulation is tricky. It should be considered alongside many other aspects of why a child reacts a certain way. In addition to behavior, emotions, and self-regulation; history, habits, trauma, and mental status can have a powerful influence on actions, too.
Keep trying – some things may feel like a roadblocks but there are specific action strategies you can use!
The Sensory Lifestyle Handbook walks you through sensory processing information, each step of creating a meaningful and motivating sensory diet, that is guided by the individual’s personal interests and preferences.
The Sensory Lifestyle Handbook is not just about creating a sensory diet to meet sensory processing needs. This handbook is your key to creating an active and thriving lifestyle based on a deep understanding of sensory processing.

Sydney Thorson, OTR/L, is a new occupational therapist working in school-based therapy. Her
background is in Human Development and Family Studies, and she is passionate about
providing individualized and meaningful treatment for each child and their family. Sydney is also
a children’s author and illustrator and is always working on new and exciting projects.







