As occupational therapy students, we had to learn bone names and all about anatomy and physiology. Naming bones comes in very handy as an occupational therapist! But, if you are working in pediatrics, kids need to learn names of bones, too! For one thing, kids learn bone names in school. But did you consider the interoception aspect to teaching bone names? When it comes to internal feelings or anatomical states that impact sensory processing and internal body actions, learning names of bones supports this awareness of self. Add this fun way to learn names of bones to your anatomy and physiology games!
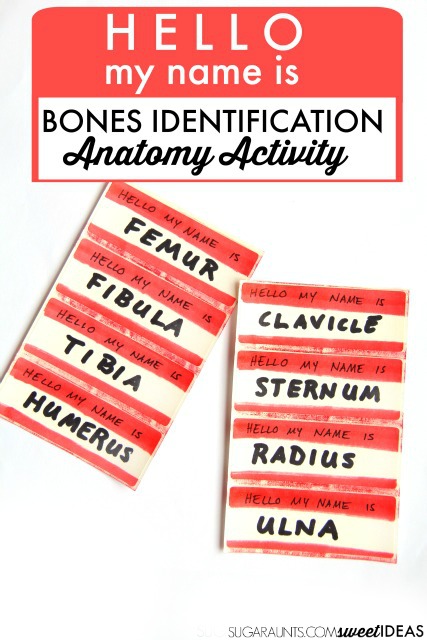
Bone Names Activity
Learning human anatomy has a special place in my heart. I mean, those semesters in Human Anatomy, Anatomy lab, and clinical kinesiology bring back fond memories.
So, when my kids ask questions like how their arm can pick up a sandwich, I have a little fun telling them about bones, joints, and muscles. This bone naming activity is just one fun way to teach bone names and teach kids about anatomy.
(Moving a sandwich is a big deal in our house!)
We’ve done a body part identification activity before, using band-aides, but these labels were a big hit with my kids. We used them to practice for a test for my big kids.
My Kindergartner and Second grader had a bones theme in their gym class, we had fun talking about the bones in our body, and made this Bone Identification and movement activity. (It would be great as a skeleton activities for preschoolers, too.
Bones Activity
This bone activity for kids is one they won’t forget…and when teaching human anatomy to kids, it’s one that will stick! The fun stickers help! 🙂
This post contains affiliate links.
I threw this activity together really quickly. We had a few sheets of blank address labels, and I grabbed a red permanent marker (affiliate link). I made a quick strip across the top and bottom of the address labels and then wrote in black marker (affiliate link), “Hello my name is” with the bone names below.
If your kids are like mine, they get a kick out of those Hello My Name Is Stickers. You could use store bought stickers, or just make your own like we did. (Amazon affiliate links)
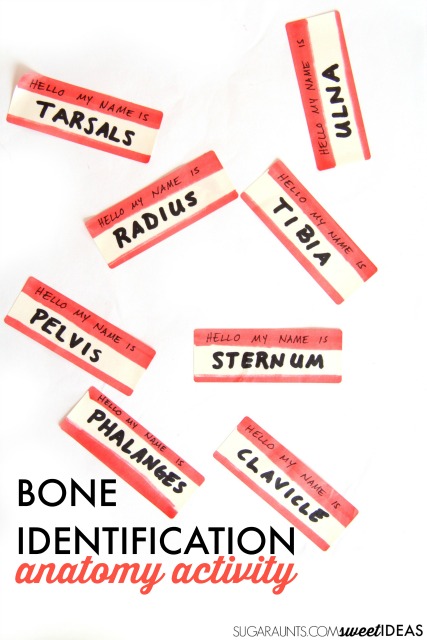
bone identification
While we used this bone identification activity with kids, it would be a great way to learn bones as part of an anatomy and physiology lesson for OT or PT students, too!
list of bones in human body
After I wrote out the names of the bones, I tested my kids on what they knew. They recalled most of the bones from gym class lessons, but we had a few that needed practicing.
For the second grade and kindergarten physical education curriculum, they had to know this list of bones in the human body:
- skull
- humerus
- radius
- ulna
- carpals
- phalanges
- clavicle
- sternum
- ribs
- pelvis
- femur
- tibia
- fibula
- tarsals
Complete List of Bone Names
Above is just a simplified list of bone names, which can be used for teaching kids about the skeletal system. A more complete list is as follows. The bone identification activity shown below can definitely be used for this complete list of bone names and bone types. Classifying and naming the entire skeletal system requires much practice, and as occupational therapists we know the power of multi-sensory learning!
Bones in the skull (includes bones in the head and face):
- Cranial bones:
- frontal bones
- Parietal bone
- temporal bones
- occipital bone
- sphenoid bone
- ethmoid bone
- Facial bones:
- mandible
- maxilla
- palatine bone
- zygomatic bone
- nasal bone
- lacrimal bone
- vomer bone
- inferior nasal conchae
Bones in the thorax:
- sternum
- ribs
Bones in the throat:
- hyoid bone
Bones in the vertebral column, or spine:
- cervical vertebrae
- thoracic vertebrae
- lumbar vertebrae
Bones in the pelvis:
- coccyx
- sacrum
- ossa coxae (hip bones)
Bones in the legs :
- femur
- patella
- tibia
- fibula
Bones in the feet:
- Ankle (tarsal) bones:
- calcaneus (heel bone)
- talus
- navicular bone
- medial cuneiform bone
- intermediate cuneiform bone
- lateral cuneiform bone
- cuboid bone
- Instep bones:
- metatarsal bone
- Toe bones:
- proximal phalanges
- intermediate phalanges
- distal phalanges
Bones in the middle ears:
- malleus
- incus
- stapes
Bones in the shoulder girdle:
- scapula or shoulder blade
- clavicle or collarbone
Bones in the arms:
- humerus
- radius
- ulna
Bones in the hands:
- Wrist (carpal) bones:
- scaphoid bone
- lunate bone
- triquetral bone
- pisiform bone
- trapezium
- trapezoid bone
- capitate bone
- hamate bone
- Palm or metacarpal bones:
- metacarpal bones
- Finger bones or phalanges:
- proximal phalanges
- intermediate phalanges
- distal phalanges
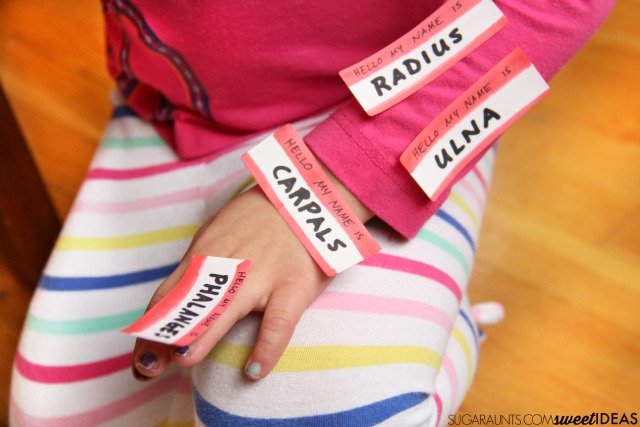

We had a blast sticking the labels all over ourselves while saying “Hello my name is humerus!” in funny voices.
While we had the labels on our body parts, we practiced the motions of that bone. We talked about how that bone could move and what it could do.
Yes, your humerus has a job in picking up a sandwich! (This is a very important fact when teaching bone names to preschoolers!)
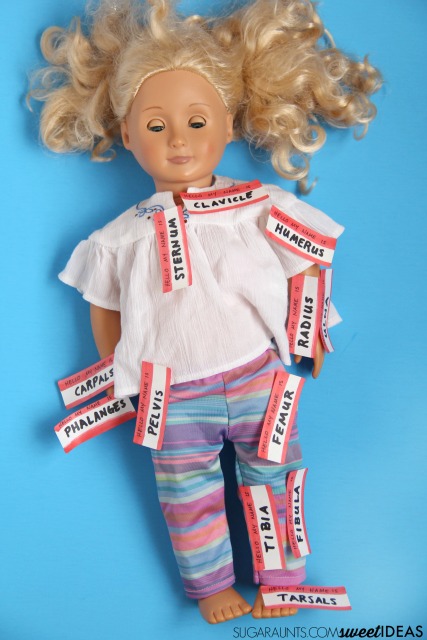

Even the baby doll got in on the bone labeling action.
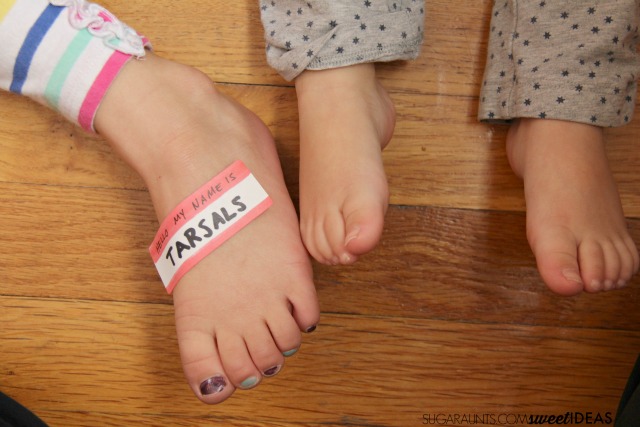

How cute are those tarsals??

Colleen Beck, OTR/L has been an occupational therapist since 2000, working in school-based, hand therapy, outpatient peds, EI, and SNF. Colleen created The OT Toolbox to inspire therapists, teachers, and parents with easy and fun tools to help children thrive. Read her story about going from an OT making $3/hour (after paying for kids’ childcare) to a full-time OT resource creator for millions of readers. Want to collaborate? Send an email to contact@theottoolbox.com.