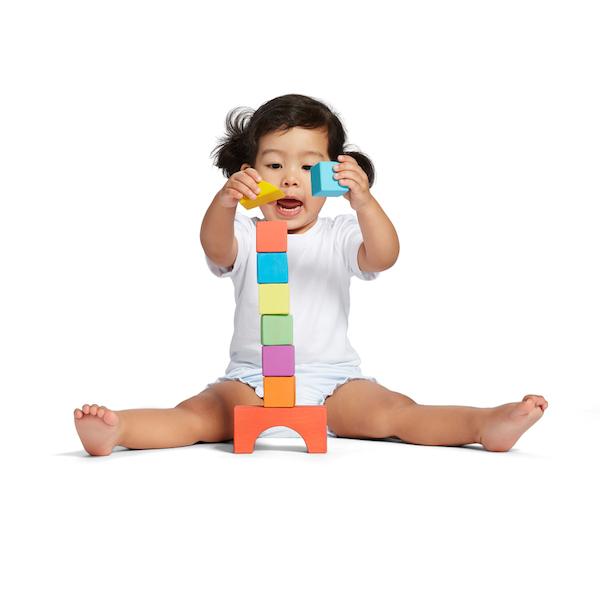
Welcome to a winter wonderland on the farm! In today’s blog post, we’re diving into the magical world of sensory play with a snowy farm sensory bin. This delightful activity combines the charm of a farm theme with the sensory joys of winter, creating an engaging and therapeutic experience for children. This is one of our favorite winter sensory bins because you can focus on so many different underlying skills through play.

Whether you’re a parent looking for creative winter activities or a therapist seeking effective tools for skill development, this farm sensory bin is tailored to captivate young minds while addressing various therapeutic areas. Read all about sensory bins in general as a therapy tool to support skill development.
Farm Sensory Bin
We love a great occupational therapy sensory activity because cold winter temps and less daylight hours mean you might not have a chance to get little ones outside as often as you might like. Plus, a farm sensory bin goes great with a Farm theme in preschool or in occupational therapy sessions.
This farm sensory bin has a winter theme, but you could actually set up a farm sensory bin any time of year. In fact, we loved this play dough farm activity that goes along with a farm theme and supports fine motor skills as well as sensory input.
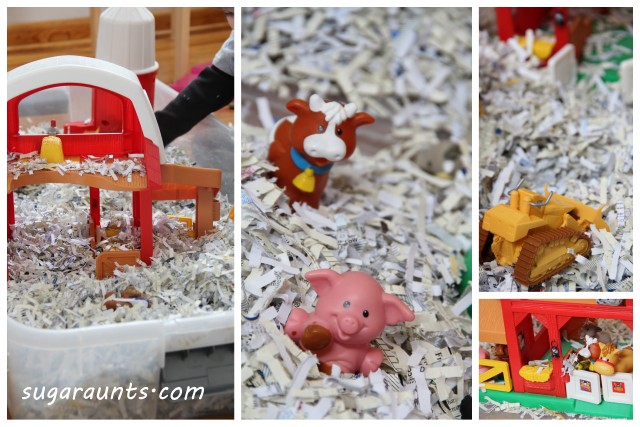
The base of shredded paper sets the stage for a snowy landscape, providing a tactile experience that stimulates sensory exploration and fine motor skills.
This winter-themed sensory bin features a collection of farm toys and mini figures, turning the snowy setting into a farm scene ready for imaginative play.
Farm Animal Sensory Bin
The farm animal sensory bin takes the excitement a step further, introducing miniature figures of beloved farm animals. As children dive into the bin, they engage in hands-on exploration, feeling the textures of the shredded paper, maneuvering the farm toys, and creating their own farm stories.
This sensory-rich experience enhances tactile input, encouraging self-confidence as children express themselves through play.
Farm Theme Sensory Bin Setup
Setting up the farm theme sensory bin is a breeze:
- Begin with a large container filled with shredded paper to create a snowy base. You could also use other sensory bin base materials if you don’t have shredded paper on hand.
- Add farm toys such as barns, tractors, and mini figures of animals to bring the farm to life.
- Encourage creativity by incorporating small props like faux trees or fences. This simple yet effective setup provides a canvas for endless imaginative scenarios.
Before this weekend, we’ve had a super cool spring. With a handful of days where it snowed. We are ready for outside play in short sleeves, running in the yard, and grass stained knees.
But, we have been loving this fun play activity too 🙂
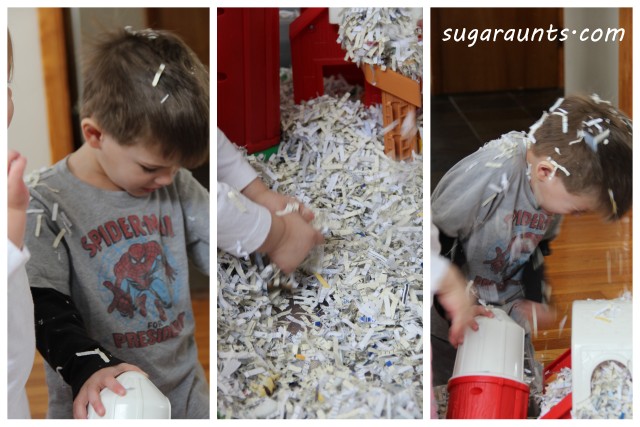
We had a boat load of shredded paper from doing taxes recently. It came in pretty handy for a small world snowy farm scene!
We put some farm animals, the Little People barn, and of course, Little Guy’s construction vehicles.
(how else can the farmer move allll that snow??)
Little Guy went to farm-town with imagination stories and pretend play.
Baby Girl loves to make the animal sounds and had a blast finding them in the shredded paper.
Why This Farm Sensory Bin Helps Development
Beyond simply playing in the sensory bin, this farm sensory bin serves as a therapeutic tool to foster development in various areas.
You can target areas in:
- Fine motor skills (Here are other winter fine motor activities to try!)
- Coordination
- Visual motor skills
- Tactile experience
- Sellf-confidence
- Imagination play
- Communication
- Bilateral Coordination- sensory bins are a great bilateral coordination activity for kids. Here is more info on Winter Bilateral Coordination Activities.
- Mindfulness- playing in a sensory bin can be calming and regulating for kids. Read about Winter Mindfulness Activities for more information.
- So much more
Fine motor skills are particularly important in early childhood development, as they lay the foundation for more complex tasks in the future.
Tactile discrimination, exploration, and sensory desensitization are effectively addressed with sensory bins as they are playful and present in a non-threatening way. The playful nature of sensory bins allows children to control their tactile experiences, fostering confidence in their interactions with materials and gradually increasing their comfort with different sensations.
The hands-on nature of the activity promotes fine motor skills as children manipulate the farm toys and engage with the sensory materials. Communication skills blossom as they create farm narratives, fostering language development.
In addition, occupational therapy providers love sensory bins because they can offer a unique and enjoyable way to engage reluctant children who may initially be hesitant about engaging in the sensory elements of tactile defensiveness challenges.
Tactile input and sensory exploration contribute to a holistic sensory experience, supporting overall sensory processing.
Imagination Play
Pretend Play
Learning Animals
Animal Sounds
Visual Scanning
Sensory Play
Farm Sensory Bin Ideas
You can pair this farm sensory bin with other therapy ideas, too. Use some of these tools and resources to support skills like gross motor skills, coordination, brain breaks, and more:
- These Farm Brain Breaks can add movement and gross motor input to a child’s day and fit in great with a farm animal theme. Print off the cards and use them in the classroom or home.
- These heavy work cards includes a set of 8 farm themed heavy work activities that can be used as a brain break or added proprioceptive input.
- Free Farm Scissor Skills Packet
- This barn craft is fun because kids can make a barn and use it in the farm animal sensory bin.
- This Farm Fingerprint art activity supports visual closure, visual tracking, and visual scanning activity, too.
- The Farm Therapy Kit has a bunch or activities to support sensory needs, handwriting, motor skills, dexterity, and more.
Get your copy of the Farm Therapy Kit.

Colleen Beck, OTR/L has been an occupational therapist since 2000, working in school-based, hand therapy, outpatient peds, EI, and SNF. Colleen created The OT Toolbox to inspire therapists, teachers, and parents with easy and fun tools to help children thrive. Read her story about going from an OT making $3/hour (after paying for kids’ childcare) to a full-time OT resource creator for millions of readers. Want to collaborate? Send an email to contact@theottoolbox.com.